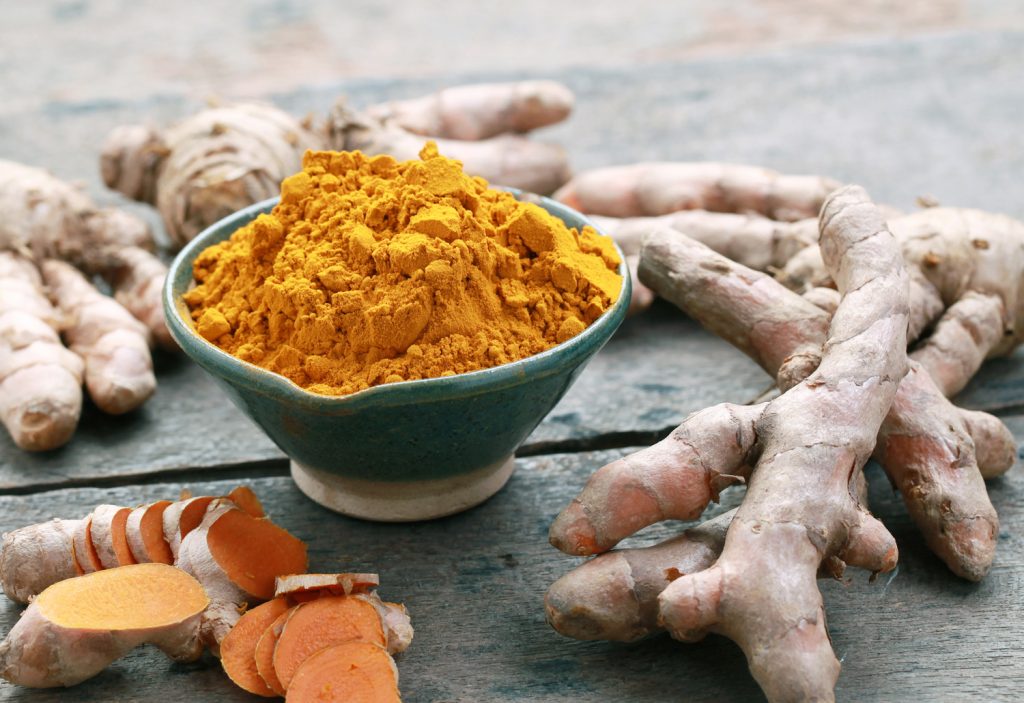
Turmeric
This is a yellow spice often used in curry that contains the anti-inflammatory oxidant curcumin. Curcumin is capable of crossing your blood-brain barrier, which is one reason why it holds promise as a neuroprotective agent in a wide range of neurological disorders.
Research has shown that curcumin may help inhibit the accumulation of destructive beta amyloids in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients, as well as break up existing plaques. Also, it has been shown that curcumin can boost memory and stimulate the production of new brain cells, a process known as neurogenesis.
Another research suggests another bioactive compound in turmeric called aromatic-turmerone which can increase neural stem cell growth in the brain by as much as 80 percent at certain concentrations. As you know, neural stem cells differentiate into neurons and play an important role in self-repair.
All these findings suggest aromatic-turmerone may help in the recovery of brain function in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and stroke. So, if you want to consume more often this super spice you should use straight turmeric powder, because some curry powders may contain very little curcumin.